Making a More Efficient Campus
Smart Campus Energy Lab

The Smart Campus Energy Lab is a small team of Electrical, Computer, and Mechanical Engineers that are working to provide the school with significant sources of renewable energy on the campus. The long-term goal is to remove the entire campus off of the grid and let it run on it’s own renewable energy sources. A secondary effort of the lab is to teach and prepare the students to work in a real-world engineering environment, allowing students to work on a real-world product.
Currently, the lab is developing sensor nodes that will be installed on the rooftops of various buildings across campus. The development process requires the students to design a device that periodically sends weather data wirelessly to a central database (called the ‘Gateway’). The students are split into teams, each developing their own design of a weatherbox. Other teams are centered around designing the housings, or developing software/firmware utilities.
Team Guava
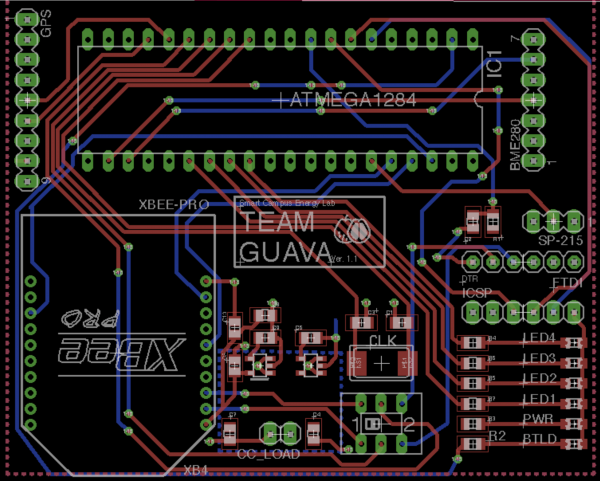
I led a team within the Smart Campus Energy lab called Team Guava. We were tasked with developing a weatherbox device using an ATMEGA1284 microcontroller, instead of the lab’s standard ATMEGA328. The reason for this is that the 1284 provides more computing power and room to expand the array of sensors on the device. From the ground up, our team designed the electrical circuits and application software for the device. We used tools such as AutoDesk’s Eagle and Digi’s XTCU to help develop this product.
Personally, I oversaw the project and developed most of the electrical schematic and printed circuit board design. We had to solve problems such as making sure all components and sensors are getting the proper current, or designing the PCB as small as possible to reduce the physical footprint of the device. The device itself runs on solar power, so it’s self-sustainable. It transmits it’s data wirelessly though an RF line using an XBee S2B transciever. The design has been tested and used to gather actual weather data that was used to analyze weather patterns around the campus.
Source: Team Guava’s GitHub Repository